Deep Vein Thrombosis

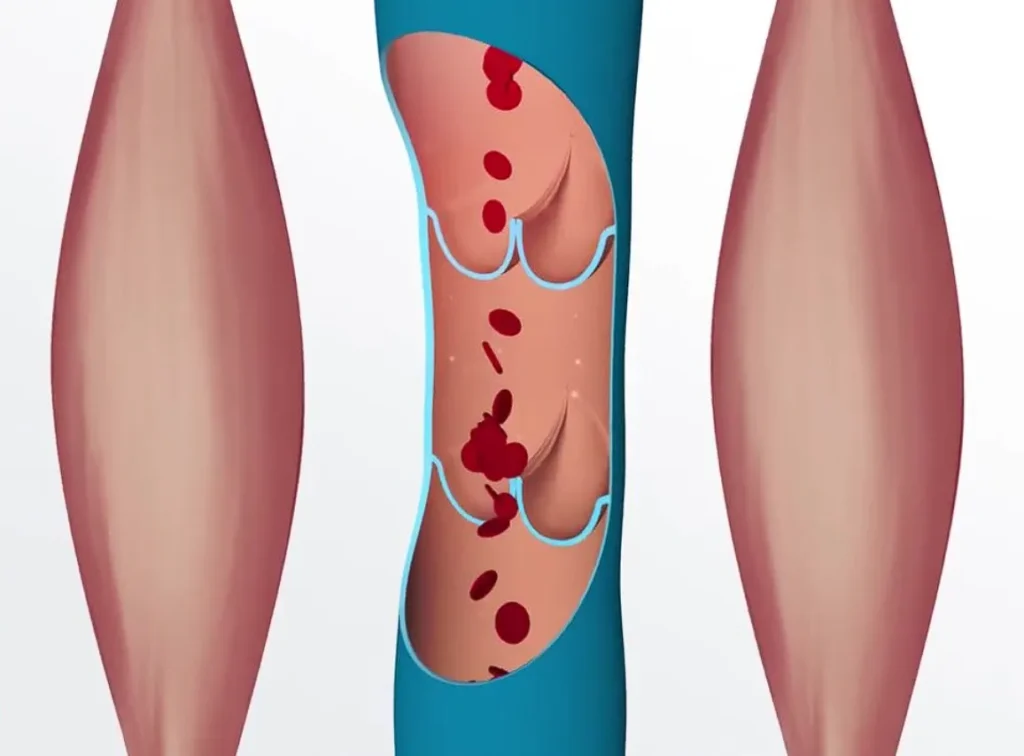
What is Deep Vein Thrombosis?
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a condition in which a blood clot, or thrombus, forms in a blood vessel, partially or entirely blocking blood flow. Blood clots commonly develop in the veins of the legs and pelvis, which transport blood from the feet, legs, and pelvis back to the heart. If you suspect DVT, it’s crucial to consult a doctor immediately, as prompt treatment is essential.
One of the severe risks associated with DVT is the potential for a pulmonary embolism. This occurs when a clot in a deep vein breaks loose and travels to the lungs, where it can block a blood vessel and become life-threatening. Clots that form in superficial veins are generally less risky, as they would need to travel to the deep veins before posing a threat.
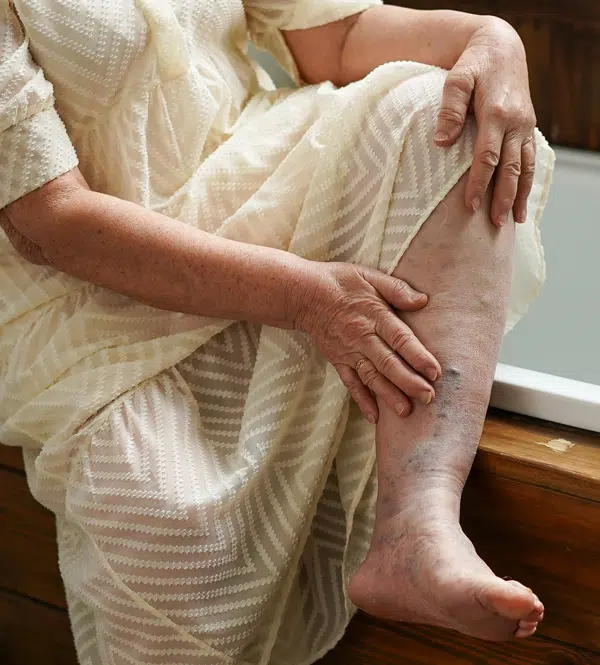
Who is at Risk for Deep Vein Thrombosis?
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) can affect individuals of all ages, but certain factors increase the risk. In younger individuals, women are more commonly affected than men due to factors such as hormonal influences and lifestyle choices. In older people, men and women share similar risk levels for DVT. Common risk factors include:
- Pre-existing Venous Disease: Conditions that weaken or damage veins increase the likelihood of clot formation.
- Coagulation Disorders: Genetic or acquired disorders that affect blood clotting can lead to a higher risk of DVT.
- Birth Control Pill Usage: Hormonal contraceptives can increase the risk of blood clots.
- Pregnancy: Pregnancy causes hormonal changes and pressure on veins, raising the risk of DVT.
- Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and affects blood flow, increasing the risk.
- Overweight: Excess weight puts added pressure on the veins, especially in the legs.
- Operations: Surgical procedures, particularly those on the legs, pelvis, or abdomen, can increase DVT risk.
- Confinement to Bed: Prolonged immobility, such as bed rest, slows blood flow, which can lead to clotting.
- Unusual Physical Exertion: Intense physical activity or trauma can lead to vein injury, increasing DVT risk.
Understanding these risk factors can help in taking preventative measures and consulting a doctor if any symptoms of DVT arise.
How You Can Prevent Deep Vein Thrombosis (Thrombosis Prophylaxis)
Preventing deep vein thrombosis (DVT) focuses on improving blood flow in the veins, particularly in the legs. While your doctor will determine the specific medications and dosages best suited to your needs, physical measures play a crucial role in thrombosis prevention. Here are some effective methods:
- Medical Thrombosis Prophylaxis Stockings: These standardized compression stockings improve blood flow by applying consistent pressure, promoting venous return, and reducing the risk of clot formation.
- Circular Bandaging: A non-standardized compression technique where the leg is wrapped to encourage blood flow. It requires skill to apply correctly and may be recommended in specific situations by healthcare professionals.
- Lower Leg Wrap-Around Compression Systems: These wrap-around systems provide adjustable compression to the lower leg. They’re handy for individuals who need flexible yet effective compression to promote blood circulation.
Compression therapy is an effective strategy for preventing DVT, especially when combined with guidance from healthcare professionals. At Innovative Therapy PC, we offer custom-fit Mediven® compression solutions tailored to your unique needs, helping you stay proactive in preventing DVT.

How to Treat Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)?
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) can be particularly dangerous, as many patients may not notice severe symptoms initially. This poses a risk because the blood clot causing DVT can dislodge and travel to the lungs, resulting in a life-threatening pulmonary embolism. Treatment for DVT prioritizes the following objectives:
- Stopping the Thrombosis from Growing
- Removing the Thrombosis
- Preventing a Pulmonary Embolism
- Preventing Post-Thrombotic Syndrome (permanent damage to venous valves)
Treatment Strategies for DVT Include:
- Basic Measures: Proper positioning, gradual mobilization, and compression therapy are vital components. Compression therapy supports venous return, helping to reduce swelling and improve blood flow.
- Medication: Blood thinners, such as heparin or Marcumar, are prescribed to prevent further clotting and reduce the risk of the clot growing.
- Thrombolysis: This treatment involves administering drugs to break down the blood clot (thrombus) directly, usually in more severe cases.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove the clot and physically restore normal blood flow.
At Innovative Therapy PC, we provide tailored compression solutions in collaboration with Mediven® to support effective DVT treatment. Custom-fit compression garments can play a crucial role in reducing the risk of post-thrombotic syndrome, improving blood flow, and supporting overall recovery.
How to Treat Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) with Compression Therapy?
Once a patient is diagnosed with deep vein thrombosis (DVT), compression therapy is often prescribed alongside medication. Compression garments apply gentle, controlled pressure on the veins from the outside, reducing their diameter and promoting quicker blood flow back to the heart.
The compression garments follow a controlled gradient—the pressure is most substantial at the ankle and gradually decreases up the leg, helping to prevent blood from pooling in the lower extremities. Over time, this improves blood circulation and reduces swelling, aiding in the recovery process and reducing the risk of complications.
Doctors will regularly assess the patient’s progress to determine if blood flow is still impaired. Based on these evaluations, your doctor will advise whether to continue wearing compression garments or if you can stop using them.
At Innovative Therapy PC, we provide custom-fit Mediven® compression garments tailored to each patient’s specific measurements and needs. By ensuring a precise fit, we maximize comfort and therapeutic effectiveness, helping patients manage DVT effectively and improve their quality of life.

The Dangers of Not Treating Deep Vein Thrombosis: Pulmonary Embolism
When a blood clot forms in a deep leg vein, blood pools, leading to vein inflammation and pain. The complications associated with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) can be hazardous. If parts of the blood clot break free, they can travel through the bloodstream to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism. This life-threatening condition blocks blood flow to the lungs, impairing oxygen exchange in the body.
The risk of pulmonary embolism is exceptionally high within the first three to five days after the onset of DVT. For this reason, prompt treatment is crucial to prevent complications and ensure adequate recovery.
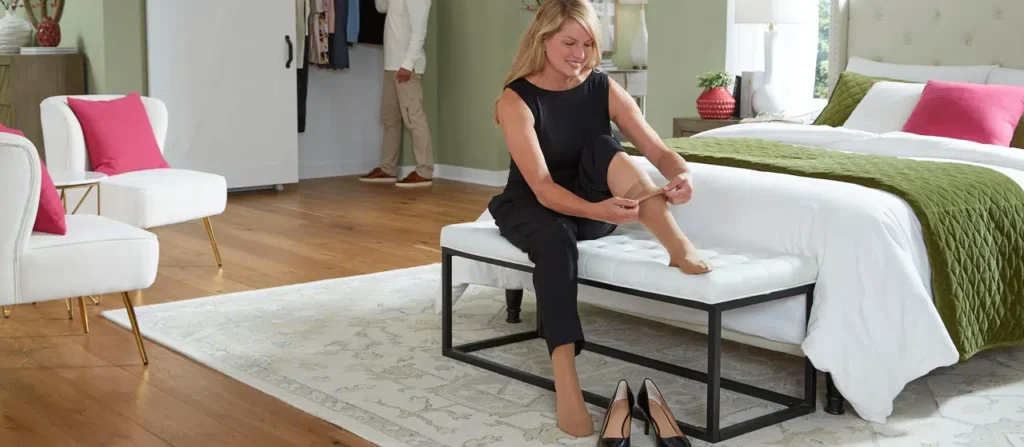

Compression Stockings – Aiding in the Prevention of Pulmonary Embolisms
Compression stockings are commonly prescribed to help prevent deep vein thrombosis (DVT), particularly after surgeries or events like a stroke, where there is an elevated risk of blood clot formation. These stockings are essential for enhancing circulation and supporting leg health, especially when mobility is limited.
Compression stockings work through graduated compression, which applies the most pressure at the ankle and gradually decreases up the leg. This gradient pressure encourages blood to move upwards through the veins toward the heart, preventing blood from pooling in the lower extremities and reducing the risk of clot formation that could lead to a pulmonary embolism.
At Innovative Therapy PC, we offer custom-fit Mediven® compression stockings designed to ensure maximum comfort and therapeutic benefit. By improving circulation, our compression solutions play a vital role in DVT prevention, helping reduce the risk of pulmonary embolism and supporting overall vascular health.
