Varicose Veins

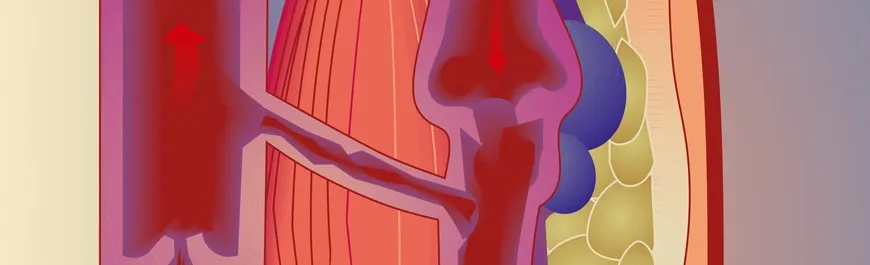
What are Varicose Veins?
Varicose veins, also known as varices, varicoses, or varicosities, are swollen, distended veins that often appear as twisted, bulging lines or knot-like structures on the surface of the skin. These veins typically develop in the legs and result from weakened or damaged valves that allow blood to pool instead of returning efficiently to the heart.
What Happens if Varicose Veins Are Left Untreated?
If varicose veins are left untreated, they can lead to serious health issues, particularly if they progress into chronic venous insufficiency. This condition impacts blood circulation and may result in:
- Skin Changes: Darkening or discoloration of the skin, usually around the ankles.
- Eczema: Itchy, inflamed skin that can develop in areas affected by poor circulation.
- Painful Venous Ulcers: Open sores that develop as a result of inadequate blood flow and can be challenging to heal.
- Open Venous Leg Ulcers (Ulcus Cruris): Advanced ulcers that can form as a result of persistent blood pooling and skin breakdown.
In severe cases, untreated varicose veins can lead to thrombophlebitis (inflammation of the veins) and blood clot formation (thrombosis), which may cause a pulmonary embolism if a clot dislodges and travels to the lungs. This can be life-threatening and requires urgent medical attention.
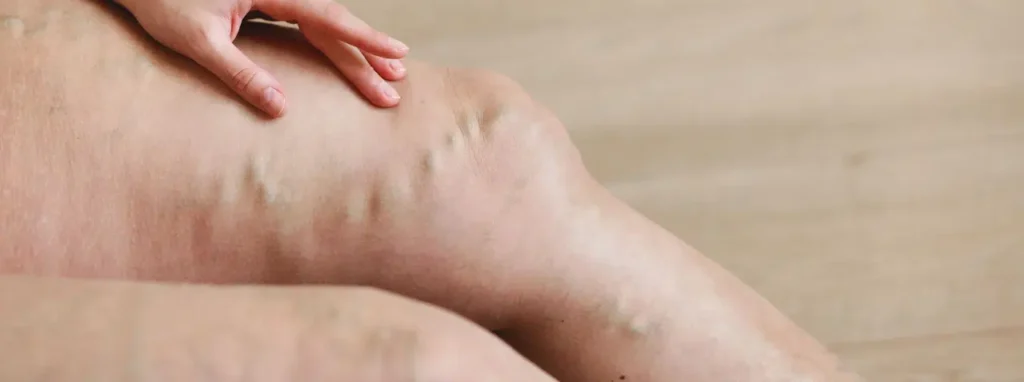
How are Varicose Veins Treated?
The blood from abdominal organs initially passes through the portal vein into the liver, where it is filtered.
While varicose veins are not entirely preventable, improving your circulation and muscle tone can reduce your risk of developing them.
Medical compression stockings are a disease-modifying treatment for varicose veins. These stockings apply mechanical pressure to the veins, reducing the venous diameter and allowing blood to flow more efficiently. Thanks to a pressure gradient that decreases from the ankle upward, blood no longer pools in the legs.
Preventive Measures
The most effective way to prevent varicose veins and other venous diseases is by consistently wearing medical compression garments with mild compression (e.g., compression class 1).
Investing in these garments offers long-term health benefits, as they can last at least six months with proper maintenance. Additionally, if medically necessary, your doctor can prescribe compression garments to support your vein health.
When is it Recommended to Wear Preventive Compression Stockings?
Wearing preventive compression stockings is advisable in the following situations:
- Hereditary Lax Connective Tissue: If you have a family history of varicose veins or other venous diseases, you may be more prone to developing them.
- Jobs Involving Long Periods of Sitting, Standing, or Squatting: Occupations that limit movement can hinder the function of the joint and muscle pumps, which are essential for healthy blood flow in the veins.
- Chronic Constipation: Increased pressure in the abdominal cavity due to constipation can put added strain on the veins.
- Frequent Alcohol Consumption: Alcohol dilates veins, increasing the risk of venous issues.
- Pregnancy, Postpartum, or Hormonal Treatments: Hormonal changes during pregnancy, after childbirth, or with the use of contraceptives or menopause treatments can contribute to varicose veins.
- Special Situations with Extended Sitting or Standing: Long journeys (such as on airplanes) or work shifts that require prolonged standing can increase the risk of venous problems, even for those with otherwise healthy veins.
Corrective Treatment Options
Corrective treatments are available for cases where preventive compression alone is not sufficient. These minimally invasive procedures are typically performed in a physician’s office with localized anesthetics, and most patients can resume normal activities within a few days.
