I’ve seen firsthand how manual therapy in sports rehabilitation can be a game-changer for athletes dealing with pain, stiffness, or limited movement after an injury. When muscles feel locked up or joints aren’t moving right, it can delay recovery and even lead to further complications. Many athletes struggle with getting back to peak performance, especially when standard treatments don’t fully address the issue.
That’s where manual therapy makes a real difference. It’s a hands-on approach that targets the root cause of the problem. Whether it’s tight muscles, joint restrictions, or soft tissue injuries. In my experience, combining manual techniques with active rehab helps reduce pain, improve flexibility, and speed up the healing process without relying heavily on medication or invasive procedures.
If you’re curious about how manual therapy actually works and how it fits into a complete sports rehab plan. I’ll walk you through everything you need to know.
Understanding Manual Therapy in Physiotherapy
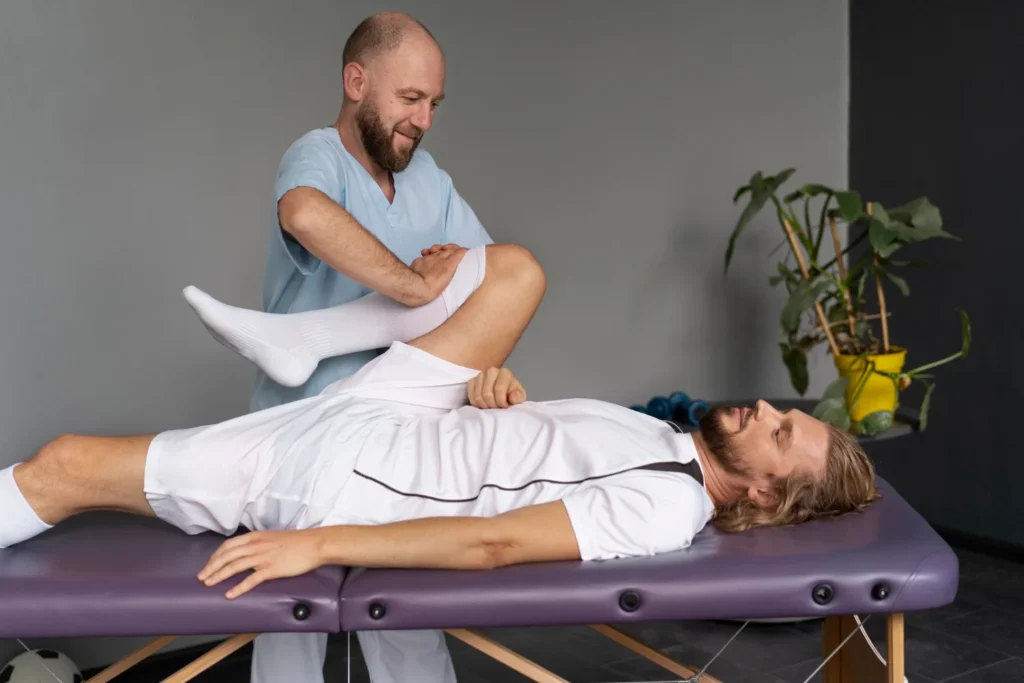
Manual therapy is a specialized, hands-on treatment used by physical therapists to assess, diagnose, and treat musculoskeletal disorders. It involves applying controlled pressure to joints, soft tissues, and muscles to improve mobility, reduce pain, and restore functional movement.
In sports rehabilitation, manual therapy plays a key role by focusing on the body’s natural mechanics. Rather than depending solely on machines or exercises, therapists use their hands to manipulate and mobilize the affected area. Techniques may include joint manipulation, myofascial release, trigger point therapy, and deep tissue massage.
Historically, manual therapy has roots in ancient medicine but has evolved with modern science. Today, it’s backed by research and supported by organizations like the American Physical Therapy Association (APTA). When performed correctly, manual therapy aligns with evidence-based practices and complements exercise-based rehab for a faster and safer recovery.
Why Manual Therapy Is Effective in Sports Injury Recovery
One of the biggest challenges athletes face is the time it takes to recover after an injury. Muscle tears, ligament sprains, or joint misalignments don’t just cause pain. They affect performance and can lead to long-term damage if not treated properly.
Manual therapy speeds up healing by:
- Increasing blood flow to the injured area
- Reducing inflammation and swelling
- Improving muscle flexibility
- Realigning joints and soft tissue structures
For athletes, the result is clear: they return to play faster, with less risk of reinjury. This hands-on approach helps reset the body’s mechanics, improves proprioception (body awareness), and enhances neuromuscular function, crucial for athletes in high-performance settings.
Top Manual Therapy Techniques Used in Sports Rehab
Different techniques are used depending on the type of injury and athlete’s condition. Here are the most commonly used and effective manual therapy techniques:
- Joint Mobilization: Gentle gliding of joint surfaces to improve movement and relieve pain.
- Myofascial Release: Relieves tension in the fascia (connective tissue) surrounding muscles.
- Trigger Point Therapy: Targets tight, painful muscle knots to restore flexibility and relieve pain.
- Deep Tissue Massage: Breaks down adhesions and scar tissue while improving circulation.
- Muscle Energy Technique (MET): Uses controlled muscle contractions to improve joint mobility.
- Soft Tissue Mobilization: Breaks up fibrous tissue and promotes healing in damaged muscle areas.
These techniques can be used independently or in combination for best results.
Sports Injuries Commonly Treated with Manual Therapy
Manual therapy is highly effective for treating a wide range of sports-related injuries. Below is a table that outlines specific injuries and the corresponding manual therapy techniques that are commonly used.
| Injury | Manual Therapy Technique | Expected Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| ACL Sprain | Joint Mobilization, MET | Improve knee mobility, reduce pain |
| Rotator Cuff Injury | Myofascial Release, Soft Tissue Mobilization | Increase range of motion, reduce stiffness |
| Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) | Trigger Point Therapy, Deep Tissue Massage | Relieve muscle tension and inflammation |
| Hamstring Strain | Deep Tissue Massage, MET | Enhance flexibility, speed up healing |
| Achilles Tendonitis | Soft Tissue Mobilization | Reduce swelling, prevent reinjury |
| Lower Back Pain | Joint Mobilization, MET | Restore alignment, reduce tightness |
What Makes Manual Therapy Unique in Sports Rehabilitation
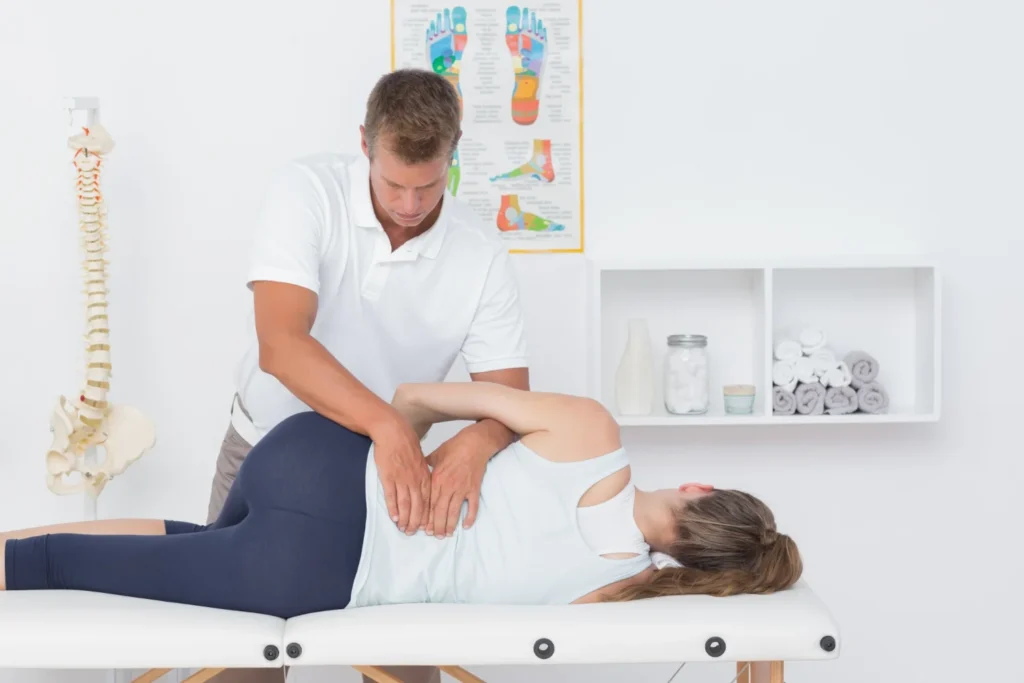
Unlike passive modalities such as heat or ultrasound therapy, manual therapy actively engages the body’s structures through skilled hands-on treatment. It’s highly personalized and responsive. If something isn’t working, adjustments can be made in real-time.
Manual therapy also emphasizes:
- Functional Recovery: Not just pain relief, but restoring how the body moves.
- Neurological Reconnection: Re-establishing brain-muscle communication.
- Tissue Remodeling: Breaking down scar tissue and promoting natural regeneration.
This comprehensive approach gives manual therapy an edge, especially in sports settings where performance and precision matter.
When Manual Therapy May Not Be the Right Choice
Although manual therapy has many benefits, it’s not suitable for everyone or every condition. Caution should be taken in the following cases:
- Acute fractures
- Active infections
- Severe osteoporosis
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
- Advanced neurological disorders (without physician clearance)
In these scenarios, manual therapy may worsen the condition or delay healing. Always consult a licensed physiotherapist or physician before beginning any manual therapy program.
Pairing Manual Therapy with Other Sports Rehab Techniques
Manual therapy is most effective when integrated into a full rehabilitation plan. Below are techniques that often work synergistically:
Combined Techniques:
- Therapeutic Exercises: Improves strength and mobility.
- Cryotherapy (Ice Therapy): Reduces acute inflammation.
- Dry Needling: Targets deep trigger points for lasting relief.
- Electrotherapy (TENS/EMS): Stimulates muscle contraction and pain relief.
| Rehab Phase | Manual Therapy Focus | Complementary Techniques |
|---|---|---|
| Acute Phase (0–7 days) | Gentle mobilization, pain relief | Ice therapy, rest, electrotherapy |
| Sub-Acute Phase | Soft tissue work, ROM exercises | Stretching, massage, dry needling |
| Recovery Phase | Joint mobilization, MET | Resistance training, proprioception drills |
| Performance Phase | Sports-specific manual release | Plyometric drills, neuromuscular training |
By layering these methods, athletes experience a more complete and faster recovery process.
Research-Backed Benefits of Manual Therapy
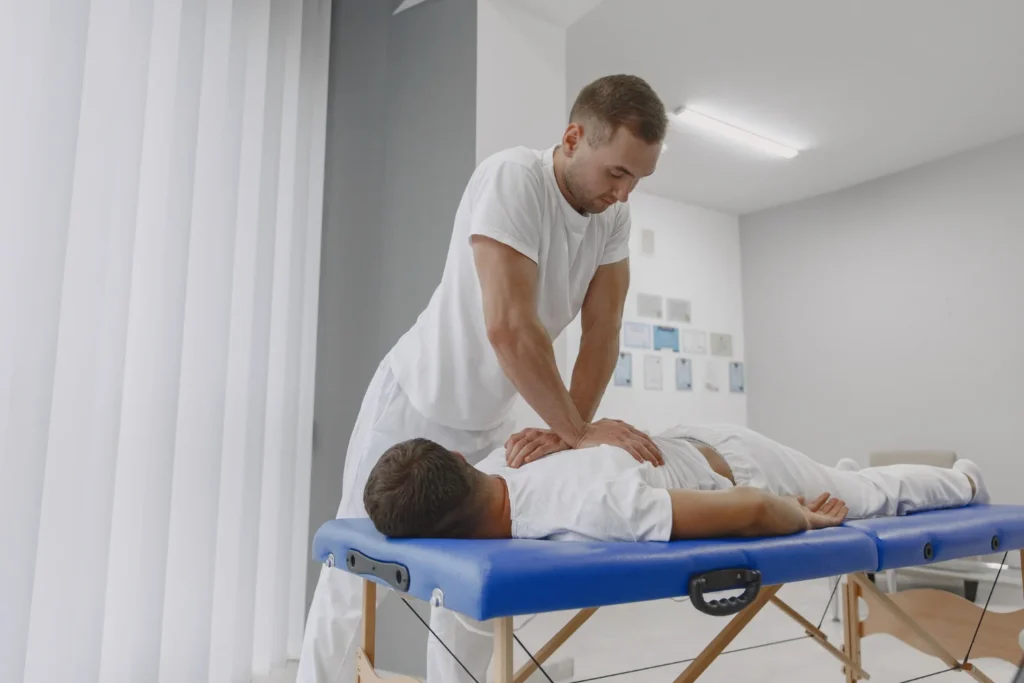

Scientific studies continue to confirm what athletes and therapists have known for years, manual therapy works.
Key Findings:
- A 2023 study published in the Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy showed that athletes with knee injuries who received manual therapy alongside exercise rehab returned to play 25% faster than those using exercise alone.
- Research from The British Journal of Sports Medicine noted improved flexibility, reduced pain, and better joint function in patients treated with trigger point therapy.
- The American Physical Therapy Association (APTA) endorses manual therapy as an evidence-based method for musculoskeletal rehab.
The evidence is clear: manual therapy offers real, measurable benefits in a sports setting.
What to Look for in a Qualified Manual Therapist
Finding the right therapist is crucial for safety and results. Here’s what to look for:
Credentials:
- Licensed Physical Therapist (PT or DPT)
- Specialized training in manual therapy techniques
- Certifications like COMT (Certified Orthopaedic Manual Therapist)
Red Flags to Avoid:
- No physical assessment before treatment
- Reliance only on massage without diagnosis
- Lack of exercise or movement therapy integration
Always choose someone who customizes the plan to your body, injury, and sport-specific needs.
Summary: Manual Therapy as a Game-Changer in Recovery
Manual therapy is more than just a technique. It’s a powerful tool in the recovery toolbox for athletes. It addresses the root of pain, improves mobility, and speeds up recovery in a way that few other treatments can.
If you’re an athlete struggling with lingering injuries, or a coach looking for safe and effective recovery options for your team, manual therapy could be exactly what you need. When paired with the right rehab plan and a skilled therapist, the results can be fast, functional, and lasting.
Also Read : Why Pain Medication is Not Always the Best Option for Pain Relief
FAQs: The Role of Manual Therapy in Sports Rehabilitation
Is manual therapy safe for all athletes?
Yes, when done by a licensed physiotherapist. However, it’s not suitable for acute injuries like fractures or severe conditions without medical clearance.
How many manual therapy sessions are needed for recovery?
It depends on the injury, but most athletes see noticeable results within 4–6 sessions, especially when combined with active rehab.
Does manual therapy hurt during the session?
You might feel pressure or discomfort, especially with deep tissue techniques, but it shouldn’t be painful. Always communicate with your therapist.
Can manual therapy prevent future injuries?
Absolutely. By improving joint alignment and muscle function, it reduces strain and corrects movement patterns, helping to prevent reinjury.
Is manual therapy better than regular stretching or massage?
It’s more targeted and therapeutic. Unlike general massage, manual therapy uses medical-grade techniques based on injury type and biomechanics.